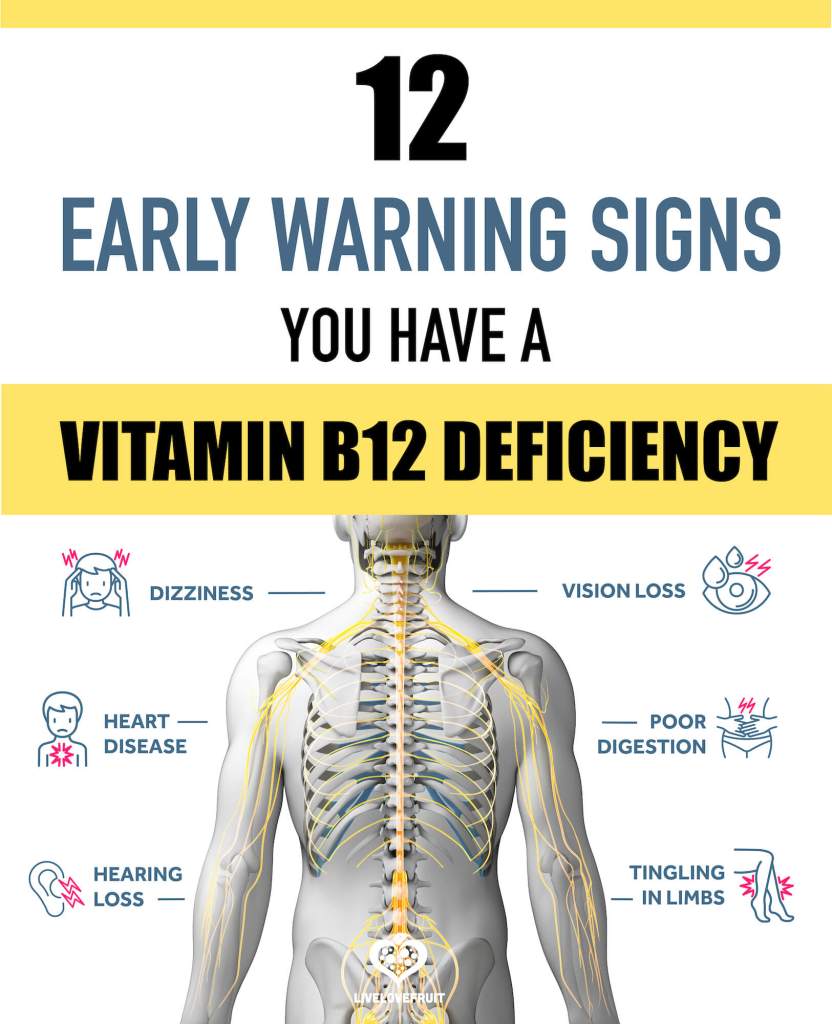
Vitamin B12 deficiency is a common issue among older adults and can lead to various health problems if left untreated. There are several reasons why older individuals may face difficulties with vitamin B12 absorption, leading to deficiency. Here are some of the challenges faced by older adults regarding vitamin B12:
- Decreased Stomach Acid Production: With age, the stomach often produces less hydrochloric acid, which is necessary for releasing vitamin B12 from the protein in food. Inadequate stomach acid can hinder the absorption of vitamin B12 from food sources, even if the diet contains sufficient amounts.
- Reduced Intrinsic Factor Production: Intrinsic factor is a protein produced by the stomach lining that binds to vitamin B12 and facilitates its absorption in the small intestine. In older adults, intrinsic factor production may decline, impairing the absorption of vitamin B12.
- Gastrointestinal Disorders: Certain gastrointestinal disorders, such as atrophic gastritis or pernicious anemia, can affect the production of stomach acid or intrinsic factor. These conditions are more prevalent among older adults and can contribute to vitamin B12 deficiency.
- Medications: Some medications commonly used by older adults, such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) or histamine-2 receptor antagonists (H2 blockers) for acid reflux or ulcers, can interfere with stomach acid production. As a result, the absorption of vitamin B12 may be compromised.
- Dietary Factors: Older adults may have dietary habits that contribute to vitamin B12 deficiency. Many individuals rely on limited food choices, which may lack sources of vitamin B12, such as meat, fish, eggs, and dairy products. Additionally, some older adults may have difficulties chewing or swallowing, making it challenging to consume foods rich in vitamin B12.
The consequences of vitamin B12 deficiency can be significant, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, anemia, memory problems, neurological impairments, and mood disturbances. Untreated vitamin B12 deficiency can result in irreversible neurological damage.
To address vitamin B12 deficiency in older adults, healthcare providers may recommend the following:
- Dietary Modifications: Encouraging a diet rich in vitamin B12 sources or recommending fortified foods and supplements can help meet the individual’s nutritional needs.
- Vitamin B12 Supplementation: Depending on the severity of the deficiency, oral or intramuscular vitamin B12 supplementation may be necessary to restore and maintain adequate vitamin B12 levels.
- Regular Monitoring: Healthcare providers should regularly monitor vitamin B12 levels in older adults, especially those at a higher risk of deficiency or experiencing symptoms. Monitoring can help detect deficiencies early and initiate appropriate interventions.
In summary, vitamin B12 deficiency is a common concern among older adults due to age-related changes in the digestive system, decreased stomach acid and intrinsic factor production, gastrointestinal disorders, medications, and dietary factors. Recognizing these challenges and implementing appropriate interventions can help prevent and address vitamin B12 deficiency, promoting better health outcomes for older individuals.
DISCLAIMER
The Site may contain (or you may be sent through the Site) links to other websites or content belonging to or originating from third parties or links to websites and features in banners or other advertising. Such external links are not investigated, monitored, or checked for accuracy, adequacy, validity, reliability, availability, or completeness by us. WE DO NOT WARRANT, ENDORSE, GUARANTEE, OR ASSUME RESPONSIBILITY FOR THE ACCURACY OR RELIABILITY OF ANY INFORMATION OFFERED BY THIRD-PARTY WEBSITES LINKED THROUGH THE SITE OR ANY WEBSITE OR FEATURE LINKED IN ANY BANNER OR OTHER ADVERTISING. WE WILL NOT BE A PARTY TO OR IN ANY WAY BE RESPONSIBLE FOR MONITORING ANY TRANSACTION BETWEEN YOU AND THIRD-PARTY PROVIDERS OF PRODUCTS OR SERVICES.
PROFESSIONAL DISCLAIMER
The Site cannot and does not contain medical/health advice. The medical/health information is provided for general informational and educational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional advice. Accordingly, before taking any actions based upon such information, we encourage you to consult with the appropriate professionals. We do not provide any kind of medical/health advice. THE USE OR RELIANCE OF ANY INFORMATION CONTAINED ON THE SITE IS SOLELY AT YOUR OWN RISK.
AFFILIATES DISCLAIMER
The Site may contain links to affiliate websites, and we receive an affiliate commission for any purchases made by you on the affiliate website using such links.
We are a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for us to earn advertising fees by linking to Amazon.com and affiliated websites.
This disclaimer was created using Termly’s Disclaimer Generator.