Care management processes refer to the systematic and coordinated approach taken by healthcare providers to ensure the delivery of high-quality, comprehensive, and patient-centered care. These processes involve various steps and activities that aim to optimize health outcomes and improve the overall healthcare experience for patients. Here are some key care management processes:
- Assessment and Identification: This initial step involves assessing the healthcare needs of individuals and identifying patients who may benefit from care management services. Healthcare professionals evaluate the patient’s medical history, current health status, and any existing chronic conditions to determine the level of care required.
- Care Planning: Once the assessment is complete, a care plan is developed in collaboration with the patient and their caregivers. The care plan outlines the goals, interventions, and strategies to address the patient’s healthcare needs effectively. It may include medical treatments, medications, lifestyle modifications, referrals to specialists, and support services.
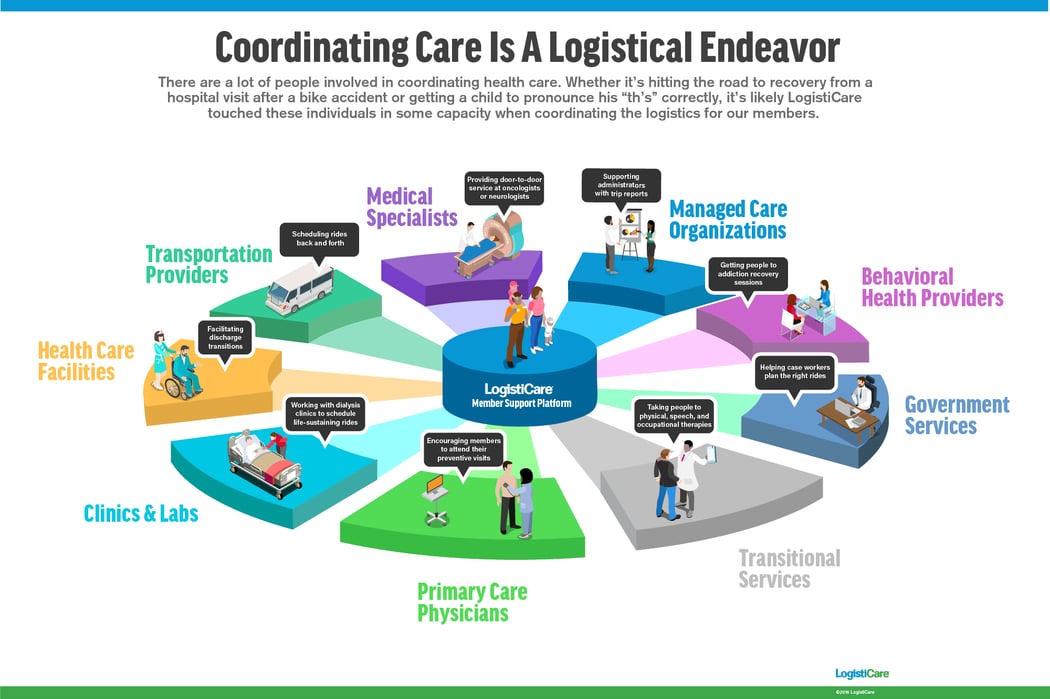
- Care Coordination: Care coordination involves ensuring seamless communication and collaboration among different healthcare providers involved in the patient’s care. This process helps to avoid duplication of services, prevent gaps in care, and promote continuity. Care coordinators facilitate the exchange of information, scheduling of appointments, and coordination of referrals and transitions of care.
- Monitoring and Follow-up: Regular monitoring and follow-up are crucial to track the patient’s progress, adherence to the care plan, and response to interventions. Healthcare providers assess the effectiveness of treatments, address any concerns or complications, and make necessary adjustments to the care plan. Monitoring may involve physical examinations, laboratory tests, and patient-reported outcomes.
- Patient Education and Self-Management: Empowering patients with knowledge and skills to actively participate in their own care is essential. Care management processes include providing education and resources to help patients understand their conditions, treatment options, and self-management strategies. This can involve teaching medication management, lifestyle modifications, symptom recognition, and encouraging healthy behaviors.
- Transitions of Care: Transitions between different healthcare settings, such as hospital to home or primary care to specialty care, require careful management to ensure continuity and prevent adverse events. Care management processes focus on coordinating these transitions, ensuring timely and accurate information transfer, and facilitating follow-up care.
- Evaluation and Quality Improvement: Continuous evaluation of care management processes is essential to measure outcomes, identify areas for improvement, and enhance the effectiveness of care. This may involve tracking clinical indicators, patient satisfaction surveys, and feedback from healthcare providers. Quality improvement initiatives are then implemented based on these evaluations to optimize care delivery.
- Population Health Management: Care management processes extend beyond individual patients to include managing the health of specific populations. This involves analyzing health data, identifying high-risk groups, and implementing targeted interventions to improve health outcomes and prevent disease.
Effective care management processes promote patient engagement, enhance care coordination, and support healthcare professionals in delivering personalized and comprehensive care. These processes are crucial for achieving better health outcomes, reducing healthcare costs, and improving the overall patient experience.